If you’re up-to-date with the financial press, you might have heard a lot of speculation in recent months about a suggested lowering of ECB-rates. The prospect of lowering the rates might make you consider whether today is the right time to make a large investment instead of waiting for the lowering of these rates. In this article, we will highlight the importance of keeping track of financial rates and how they can impact your business.
Key Take-aways
- Euribor rates are a benchmark for commercial rates.
- Keeping track of interest rates helps you to plan your future investments.
- High interest rates affect the growth of your business or the success of your investment.
Euro Interbank Offered Rate (EURIBOR)
It’s almost always harder to raise capital than you thought it would be, and it always takes longer. So plan for that.
Richard Harroch says what virtually every growing business experiences on a regular basis. The founder started with an idea, an itch if you will, but then suddenly all different kinds of teachings enter the metaphorical arena. Financing, managing, accounting, recruitment and so on. For every discipline a different doctrine. And what should they do?
Don’t worry, it’s not necessary to get a PhD for each and every discipline. A basic understanding of how “things” work will get you far in looking for a suitable partner to assist you. But first, we need a better understanding of where our money is coming from.
Tracing back the origin of our money will eventually lead us to a bank. More specifically, we would be going from one bank, to another, to the next one and maybe back again. Money is subjected to supply and demand, just like consumer goods. Banks lend money to each other and, like any other loan, they have to pay interest for it. This huge amount of money is usually named a fund and banks bid on these funds with set interest rates. However, because of the scale on which this operation works, it is necessary to regulate this lending of funds and stabilise the rate at which this money gets bought. Introduce: EURIBOR.
Each business day, a panel of approximately 20 European banks send their fund interest rates to the European Money Markets Institute. The latter discards the top and bottom 15% and calculates the average rate of the remaining entries. This average rate will be the rate presented by the Euribor. Therefore, we can consider the Euribor as a benchmark against which all other European banks can match their rates. Add a small percentage on top of the Euribor, and it becomes clear how banks earn their gross profit margins when they loan these funds to private and professional ventures.
Euribor Rates
First and foremost: Euribor rates do not apply to non-financial businesses. Yet, the Euribor rates do affect our business, as will be elaborated later on.
Out of historical data, it is possible to derive historical trends, as shown in figure 1. Before 2008, business was booming, so to speak. But in October of that same year, financial institutions began to crumble, the financial crisis began and rates started dropping. Following that crisis was the European debt crisis which was halted by Mario Draghi’s famous words: “Whatever it takes”. Many will remember the declining interest rates afterwards, which saw their turn-around in 2022.
The European Central Bank
Where does the ECB appear in this story? Remember these funds mentioned earlier. As administrator of the Euro-currency, the ECB also provides funds to commercial banks. And it virtually cannot run out of money. It has to be clear, though, the ECB does NOT set Euribor rates nor vice versa. But the policies of the ECB very much influence setting rates, by the bank panel, for the Euribor.
Figure 2 displays the historical rates of the ECB, Euribor and an indication of Belgian composite cost of borrowing. The latter is shown to indicate how commercial rates for corporations follow the general trend of the Euribor. On average, the rate at which non-financial corporations loan money from the commercial bank lies 1.75% higher than Euribor 1-month rate. This partially explains the gross profit margins of a commercial bank. However, in our experience, this additional rate can vary widely depending on how well you present your investment to the bank. A good presentation might work in your favor.
Note: between June 2000 and October 2008 the ECB used variable rates instead of fixed rates. This data was combined
Inflation, rates and the economy
Need a refresher? The Wall Street Journal explains how rates impact U.S. Economy. The same principle is in effect for the European Market, video.
The economy, or also referred to as the market, is based on the principle that anyone who is active in that market is able to participate in that particular market. An employee generates value for a company by doing work. In turn, the company can generate more value, i.e. goods or services, to sell. And the revenue generates a wage for that employee. The goal is always to create more value, often represented by money. These particpants are you and I, or anyone else in a certain region and active in that particular economy.
Another element in an economy is scarcity. At any given point in time, or seen over longer period, there is always a limitation on resources that are available. Whether it is not the right season for a certain fruit or some natural disaster messed up the supply chain of some rare-earth material, which slows down production (Remember the computer chip scarcity that influenced consumer goods and the automotive sector?). Scarcity is often the driving force for raising prices.
Then there is competition between markets. The Belgian market is a well-known chemicals market, particular pharmaceuticals (approx. $44b in 2020), and a services market (approx. $40b in 2020). These products are our economy’s export products. But the Belgian economy is also a notorious import market, currently valued at $449b vs $403b in export. One market can never provide all required goods and services, so trade necessary if growth is desired. In Europe, all regional submarkets form one big European Market.
Which brings us to inflation and recession. Inflation is the erosion of income. Let’s imagine a Monopoly game where money would be handed out very quickly, faster than some players can generate new income. Problems would soon arise. Another way of looking at inflation is that a participant of a market cannot generate income quickly enough to keep on participating in that economy because prices rise quickly and other particpants do have generated enough income. Theorethically, it becomes an extreme inequality if you will.
Recession is arguably worse. Recession cuts spending which usually leads to lay-offs. Participants without a job cannot generate any income and are likely worse off than with high inflation, where there is little income.
So this is the part where interest rates become important. In times of excessive inflation, raising interest rates will cut back spending, prices will stabilise and wages can rise in order to get everyone back on track. Otherwise, in times of relative recession, lowering the rates will stimulate the market to create work or to venture on riskier paths in order to create value. Thus it forms an incentive to spend money and hire people.
But there is a catch to it all: at the end of the day, economies are still dependent on people participating in it. Each and everyone has their own thoughts on how to participate in it. If you look back at figure 2, it could be reasoned that there were 10 years of relative recession. But the pandemic has halted markets and most particpants were able to save some money. In 2022, after COVID, everyone and all the economies wanted to be active again. Money was being spent to buy necessary goods and prices rose so that, halfway 2022, higher interest rates made all buyers think twice about whether they actually wanted to spent their money on those goods.
Influence of rates on businesses
Now let’s focus on businesses. Imagine you have found the next big thing. Likely all of your efforts are focussed on making and selling your product and/or service. Virtually every entrepreneur confesses that focussing on your product, will take all of your time. Yet business-wise, it remains important to know when to invest in your business and when to hold back. In order to give an insight in what financial experts can mean for your business, an example follows on why it is important to keep an eye on those rates.
First and foremost, there is never only one variable to take in account for successful growth or expanditure. Even if the product or service is a direct-hit and is sold out and generates maximum revenue, still, other variables in this equation can be and are not exclusive to:
- Capital: equity versus debt. How much do you own and how much is borrowed one way or another.
- Production: workforce cost, facilities, machinery and maintenance etc.
- Losses: production delays, bad times, sickness etc.
- Inflation: our minimum-required resources become more expensive, e.g. electricity bill.
- Many more…
With a simplified example, scenario 1 and scenario 2, will illustrate how two different loan rates (2% vs. 4%) can impact a business solely based on those rates. In this example, we created a sneaker business and baptised it Ekin B.V.. The bank will allow us 1-year financial assistance with a maximum of €150k. As long as our sales are good, we can expect the same conditions next year.
Our business strategy will be:
- Increase production to maximum capacity.
- If there is profit, reduce financial assistance but keep maximum production.
- Gain 50k equity.
Simplifications:
- No depreciation or amortisation is applied.
- Costs are simplified.
- Earnings are simplified.
- Rates are fixed.
Our production line is simple:
- a €50k machine with €10k maintenance fee every year after. Maximum capacity is 1500.
- Price per unit is €100, incl. all costs from resource to customer.
Note: strategy is a very important part of business. Derived from strategies are budget allocations, reinvestment options, production methods and much more. It is impossible to simplify a case while taking in account all these factors. Therefore, the above mentioned strategy is the one applied to the example.
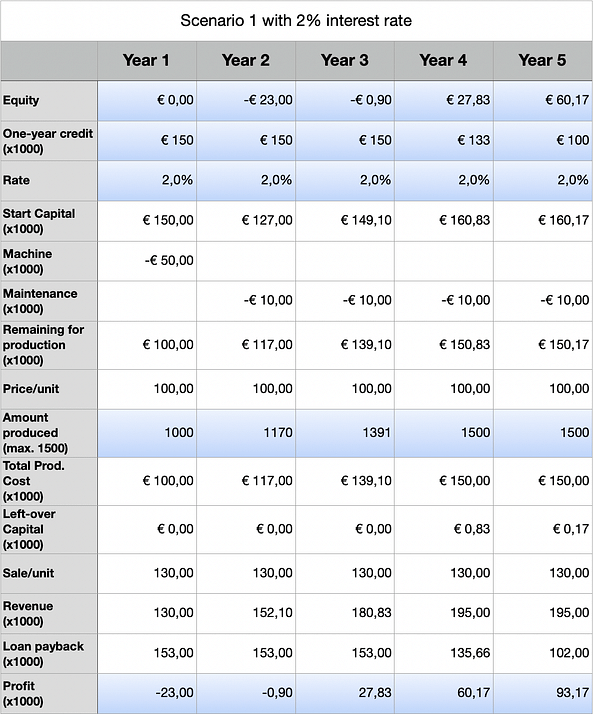
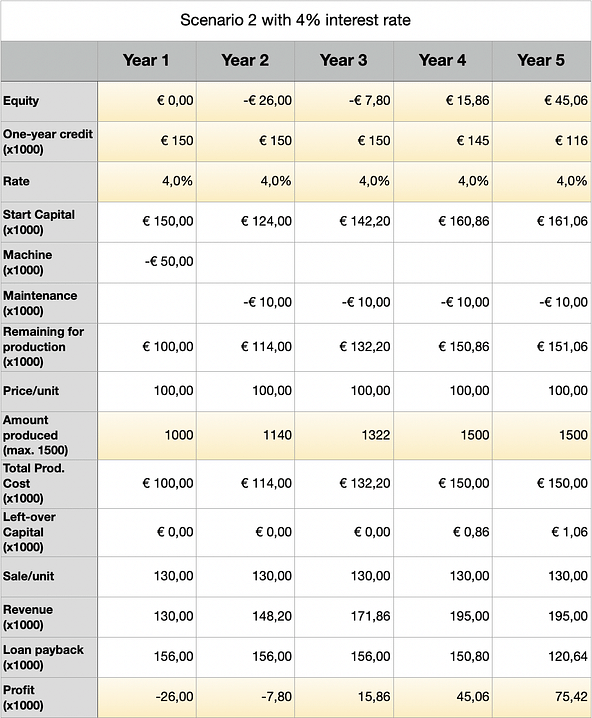
Review after five years, based on strategy
- Both scenarios managed full capacity in their fourth year, but scenario 1 did so more comfortable. The difference in production capacity for year 2 and year 3 was respectively 30 units and 69 units out of 1500 total.
- In scenario 1, the financial assistance was lowered to €100k vs. €116k in scenario 2.
- In scenario 1, the beginning of year 5, the equity exceeded €50k (>€60k). An additional machine to expand production could be considered from now on. Scenario 2 did not manage to fulfill this.
The most important keypoint to take away from this illustrative example is that interest rates on financial assistance can significantly impact a business’ decissions, growth and expanditure. Keeping track of rates helps a business to assess its future. The job market is flooded with applications for financial experts and it should be no surprise that the financial sector is estimated at $31.000 billion. This gives a little insight on why corporations heavily depend on financial expertise for keeping their business alive.
Summary
We’ve started this article with the introduction of the Euribor and describing how it forms a benchmark for future rate setting. Financial experts should be up-to-date on this rates if they wish to foresee certain trends in the economy. Although commercial rate setting is never far behind, the Euribor and ECB-rates are two early indicators on what rates will do in the future. If you combine this knowledge with relevant industry news, it can give your business a huge advantage for planning growth.
Our illustrative example showed that rates have a larger impact on the revenue than might appear at first sight. Although the payback difference for each individual year was only €3.000, the difference in revenue after five years became a whopping €17k. That ought to give your business a little extra help!
But it is also important to understand why these rates go up and down. Rate setting is a mere simple yet relative effective tool in steering economies and making sure everyone can particpate in it. And a clear understanding as to what a rise or lowering means, provides you with a more sensitive feeling of what the market is needing.
In this article, we pointed out that interest rates you might receive for your growth can be variable, even when they seem to be fixed rates. The rule of thumb would be that good preparation and clear communication with your bank can be highly beneficial for your business when looking for financing. At CFOrent, we specialise in acquiring loans for our clients while assisting them with the financial side of their businesses. Our starting point is always understanding your business and using our expertise in preparing your statements or searching for beneficial factors that’ll help convince the bank giving your business an optimal rate. Don’t hesitate to reach out here.
Data sources
Euribor historical rates
ECB historical rates
Belgian composite cost historical data
